What Are Fibroids
Home » What Are Fibroids
Understand Uterine Fibroids With Atlanta Fibroid Clinic
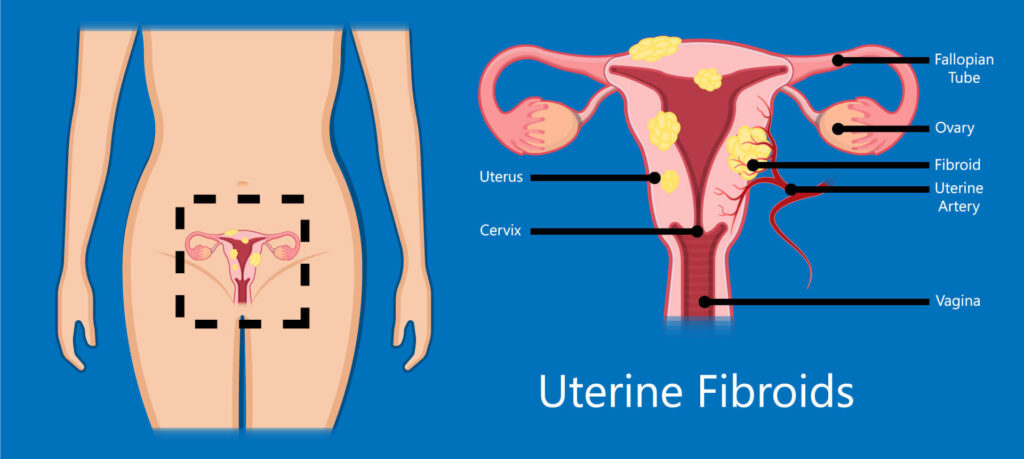
What are uterine fibroids?
Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that grow in your uterus. The medical term for fibroids is “leiomyoma” or “myoma.” Fibroids can develop individually or in clusters, ranging in size from as small as a grain of rice to as large as a grapefruit.
Women of childbearing age and those in their 50s can be affected by uterine fibroids. Some fibroids are non-symptomatic, while others cause symptoms such as abdominal bloating and pain, heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding, frequent urination, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Are there different types of fibroids?
There are 4 types of fibroids
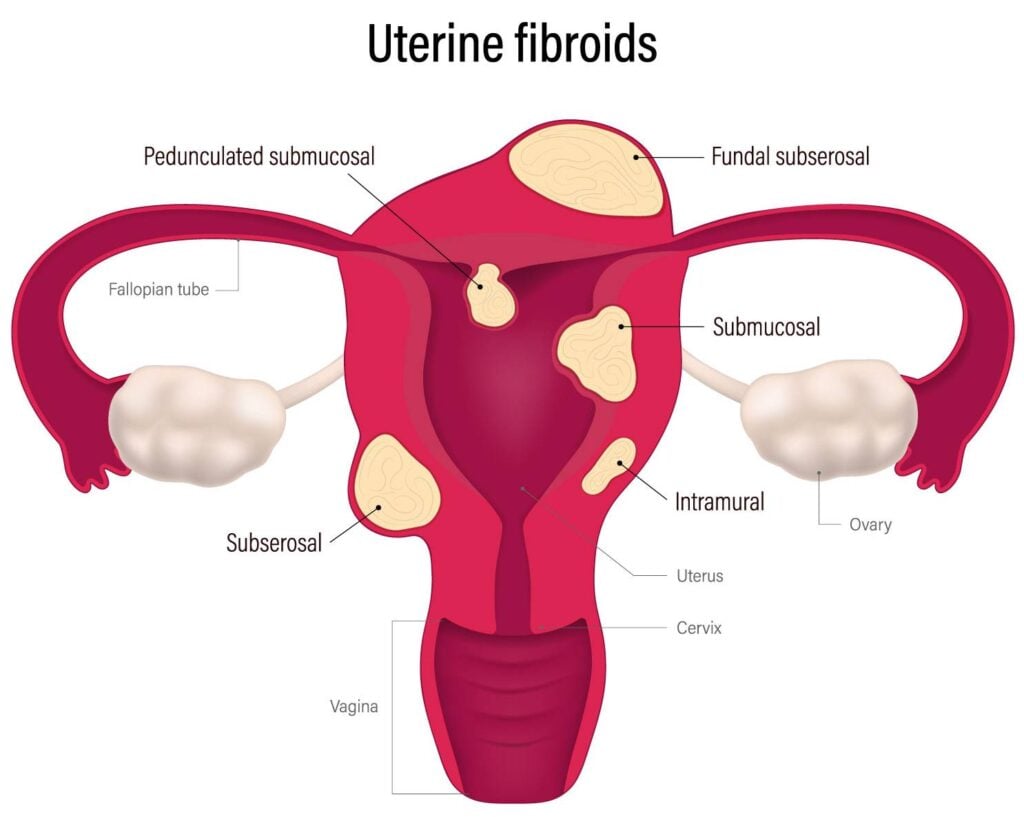
These are the most common type of fibroids – typically developing within your uterine wall and expanding from there. When an intramural fibroid tumor expands, it makes your uterus feel larger than normal, causing your abdomen to appear bloated. This is the reason why women suffering from intramural fibroids are frequently mistaken for being pregnant.
These types of fibroid tumors can also cause “bulk symptoms,” which include excessive menstrual bleeding, prolonged menstrual cycles, and the passing of blood clots. They are also responsible for pelvic pain caused by additional pressure placed on surrounding organs as the fibroids increase in size.
Subserosal fibroids typically develop on your outer uterine wall. As they grow outward, they increase in size, which puts additional pressure on your surrounding organs.
Symptoms of subserosal fibroid tumors usually do not include abnormal or excessive menstrual bleeding, nor do they interfere with your typical menstrual flow. They do, however, cause immense pelvic pain and pressure.
The least common of the various types of uterine fibroids are submucosal fibroids. These types of fibroids develop just under the lining of the uterine cavity. Large submucosal fibroid tumors may increase the size of your uterus cavity, blocking your fallopian tubes, which may in turn lead to complications with your fertility.
Symptoms associated with submucosal fibroids include heavy, excessive menstrual bleeding and prolonged cycles. These symptoms also cause the passing of heavy clots that often result in staining of clothing. Untreated, prolonged, or excessive bleeding can lead to additional complications such as anemia and/or fatigue, which could potentially set off a future need for blood transfusions.
Pedunculated uterine fibroids occur when a fibroid tumor grows on a stalk, resulting in pedunculated submucosal or subserosal fibroids. These fibroids can grow into your uterus and outside your uterine wall. Symptoms associated with pedunculated fibroid tumors include pain and pressure as the fibroids often twist on their stalk.
It is not uncommon to have multiple fibroids that are spread out in your uterus, making it difficult to pinpoint which fibroid is responsible for your symptoms.
Are there different types of fibroids?
There are 4 types of fibroids
These are the most common type of fibroids – typically developing within your uterine wall and expanding from there. When an intramural fibroid tumor expands, it makes your uterus feel larger than normal, causing your abdomen to appear bloated. This is the reason why women suffering from intramural fibroids are frequently mistaken for being pregnant.
These types of fibroid tumors can also cause “bulk symptoms,” which include excessive menstrual bleeding, prolonged menstrual cycles, and the passing of blood clots. They are also responsible for pelvic pain caused by additional pressure placed on surrounding organs as the fibroids increase in size.
Subserosal fibroids typically develop on your outer uterine wall. As they grow outward, they increase in size, which puts additional pressure on your surrounding organs.
Symptoms of subserosal fibroid tumors usually do not include abnormal or excessive menstrual bleeding, nor do they interfere with your typical menstrual flow. They do, however, cause immense pelvic pain and pressure.
The least common of the various types of uterine fibroids are submucosal fibroids. These types of fibroids develop just under the lining of the uterine cavity. Large submucosal fibroid tumors may increase the size of your uterus cavity, blocking your fallopian tubes, which may in turn lead to complications with your fertility.
Symptoms associated with submucosal fibroids include heavy, excessive menstrual bleeding and prolonged cycles. These symptoms also cause the passing of heavy clots that often result in staining of clothing. Untreated, prolonged, or excessive bleeding can lead to additional complications such as anemia and/or fatigue, which could potentially set off a future need for blood transfusions.
Pedunculated uterine fibroids occur when a fibroid tumor grows on a stalk, resulting in pedunculated submucosal or subserosal fibroids. These fibroids can grow into your uterus and outside your uterine wall. Symptoms associated with pedunculated fibroid tumors include pain and pressure as the fibroids often twist on their stalk.
It is not uncommon to have multiple fibroids that are spread out in your uterus, making it difficult to pinpoint which fibroid is responsible for your symptoms.

Choose a preferred location nearest you
Expert care in a welcoming environment for patients seeking fibroid treatment